Really Bad Ideas - Government Debt Isn’t Actually Debt
Interest-Rates / US Debt Aug 10, 2017 - 09:03 AM GMTBy: John_Rubino
 The failure of fiat currency and fractional reserve banking to produce a government-managed utopia is generating very few mea culpas, but lots of rationalizations.
The failure of fiat currency and fractional reserve banking to produce a government-managed utopia is generating very few mea culpas, but lots of rationalizations.
Strangest of all these rationalizations might be the notion that government debt is not really a liability, but an asset. Where personal and business loans are bad if taken to excess, government borrowing is not just good on any scale, but necessary to a healthy economy. Here’s an excerpt from a particularly assertive version of this argument:
What if every government paid off its national debt?
(Medium.com) – IT might make you feel better but tomorrow if the US Federal Government, or Australia or the UK repaid the entirety of its national debt, it would make not one dollar’s difference to your bank account.In fact the economy would tank.
“If America repaid all its national debt tomorrow, we very likely would crash into the mother of all great depressions long before the debt is ‘paid off’”, says economist, Professor Randall Wray.
There were six times in US history in which budget surpluses were achieved for long enough to retire a significant amount of debt. Five of those were followed by depressions, the last of which culminated in the Great Depression of the 1930s.
The last time America ran a significant budget surplus (about 2.5 years) was under President Clinton. The 2002 recession is a direct result of Clinton’s 1999 surplus which forced the domestic private sector into deficit. Consumer spending fell, unemployment rose and a recession occurred.
The economy crashed first in 2000 and then onwards into the Great Recession that began in 2007.
Economist Ellis Winningham concurs with Professor Wray that the economy would ‘crash’ long before the outstanding debt would be retired.
“The surplus would then become a deficit again,” he said.
“But reducing or retiring the debt isn’t what caused the economic downturns. It was the surpluses that caused it. Simply put, you cannot operate an economy with no money in it.”
So why have we convinced ourselves that government debt is the mother of all evil? That somehow, if the government is in surplus, our bank accounts will automatically improve?
In fact, as we shall see, the precise opposite is what would probably happen.
What is debt?
Anyone who has ever been chased by a debt collector has come to associate the word ‘debt’ as necessarily scary, bad and to be avoided. If you are a household, this is likely to be true.But debt has an entirely different meaning for governments.
To whom is the national debt owed? That would be us: the people.
But this truth has been avoided in favour of eliciting a pavlovian response based entirely on the principle that a government budget is the same as that of a household.
Let’s start with the idea that the 2000 tech stock crash was caused by the tiny (and in any event fictitious) surpluses run by the Clinton administration in the 1990s.
What actually happened in that decade was a massive increase in societal debt via the private sector – encouraged by the Federal Reserve’s decision to bail out every entity anywhere in the world that ran into financial problems. Long Term Capital Management, Russia’s default, Mexico’s peso crisis, and the Asian Contagion were all met with lower rates, loan guarantees and aggressive money printing.
The result was a torrent of hot money, much of which flowed into US tech stocks, sending their valuations to stratospheric, completely unsustainable levels (while filling government coffers with capital gains tax revenues). The inevitable crash had nothing whatsoever to do with those temporary surpluses and everything to do with equity valuations that had exceeded anything seen during even the Roaring 20s.
As the following chart illustrates, US total debt rose from 235% of GDP in 1995 to 250% in 2000, producing the tech bubble. And then it really got going as the government responded to the subsequent bust with even easier money, producing a housing bubble that in its own way was as historically extreme as the tech bubble. When this burst we got the Great Recession – which was then countered with massive increases in government debt worldwide.
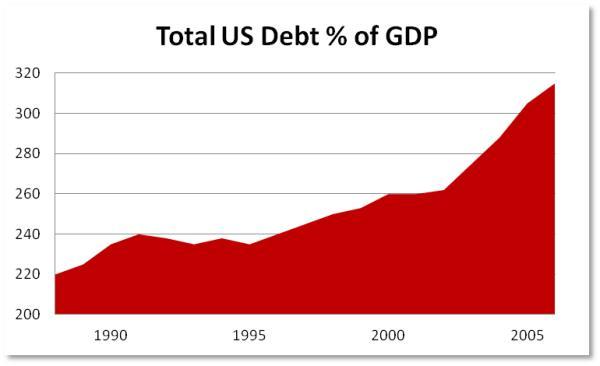
Through these booms and busts, the entity doing the actual borrowing didn’t matter. What did matter was the amount of new debt being created. The government could be the main borrower as it was post-2008 or it could use lower interest rates and loan guarantees to encourage the private sector to borrow as in the 1990s. Either way the result was a destabilizing credit bubble.
As for the assertion that governments paying off debt lead to depression, a quick stroll through US financial history paints a different picture, with long periods of more-or-less balanced budgets during which debt/GDP fell steadily.
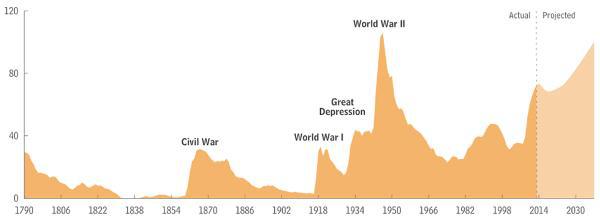
Especially interesting is the half century between the Civil War and WW I, in which government debt plunged in relation to GDP – to pretty close to zero — but the global economy grew steadily with minimal inflation. This was the age of the Classical Gold Standard in which the supply of money – and by implication the borrowing power of governments – was limited by the dominance of sound as opposed to make-believe fiat money. It was ended not by a financial crisis related to government budgets but by war and ideology — an ending that could have been avoided by a few personnel changes atop several European countries.
So here’s an alternative explanation for the relationship between government debt and financial crisis: Excessive debt in any sector – government, corporate, household, whatever – produces asset bubbles that inevitably burst, yielding recessions, depressions, and – in response – massive increases in new government borrowing. Avoid debt binges and you avoid asset bubbles and speculative manias. Avoid manias and the government has little need for crisis borrowing.
Instead of lurching to another level of New Age financial experimentation when the current bubble bursts, a historically-literate society would return to the classical gold standard and perhaps even ban government debt entirely.
But of course if we were historically literate we wouldn’t be in the current fix. So expect the “government debt not only doesn’t matter, it’s actually a form of wealth!” argument to win out during the next crisis, ushering in the final, fiery act of the fiat currency experiment.
The previous articles in this series are here and here.
By John Rubino
Copyright 2017 © John Rubino - All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



