The Japanese Deflation Myth and the Yen’s Slump
Economics / Japan Economy Sep 29, 2014 - 06:05 PM GMTBy: MISES
 Brendan Brown writes: The slide of the yen since late summer has brought it to a level some 40 percent lower against the euro and US dollar than just two years go. Yet still Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and his central bank chief Haruhiko Kuroda warn that they have not won the battle against deflation. That caution is absurd — all the more so in view of the fact that there was no deflation in the first place.
Brendan Brown writes: The slide of the yen since late summer has brought it to a level some 40 percent lower against the euro and US dollar than just two years go. Yet still Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and his central bank chief Haruhiko Kuroda warn that they have not won the battle against deflation. That caution is absurd — all the more so in view of the fact that there was no deflation in the first place.
 Some cynics suggest that Abe’s and Haruhiko’s battle cry against this phoney phantom is simply a ruse to gain Washington’s acquiescence in a big devaluation. But whatever the truth about their real intent, Japan’s monetary chaos is deepening.
Some cynics suggest that Abe’s and Haruhiko’s battle cry against this phoney phantom is simply a ruse to gain Washington’s acquiescence in a big devaluation. But whatever the truth about their real intent, Japan’s monetary chaos is deepening.
Japanese Prices Have Been Stable
The CPI in Japan at the peak of the last cycle in 2007 was virtually at the same level as at the trough of the post-bubble recession in 1992, and up a few percentage points from the 1989 cycle peak. Hence, Japan alone has enjoyed the sort of price stability as might be enjoyed in a gold-standard world. Prices have fallen during recessions or during periods of especially-rapid terms-of-trade improvement or productivity growth. They have risen during cyclical booms or at times of big increases in the price of oil.
If price-indices in Japan were adjusted fully to take account of quality improvements they would have been falling slightly throughout, but that would also have been the case under the gold standard and was fully consistent with economic prosperity.
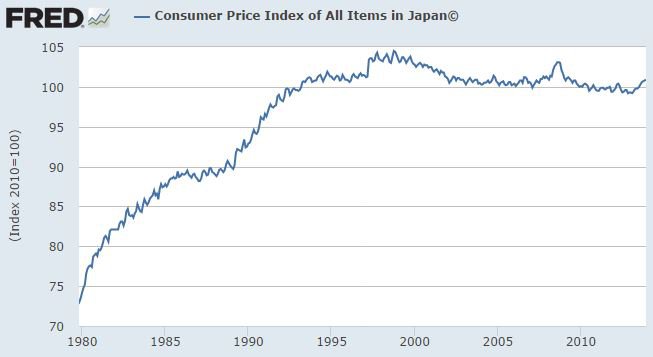
Such swings in prices are wholly benign. For example, lower prices during recession coupled with expectation of higher prices in expansion induce businesses and households to spend more. A valid criticism of the Japanese price experience of the past two decades has been that these swings have lacked vigour due to various rigidities. Particularly valid is the claim that price falls should have been larger during the post-bubble recession of 1990-93 and subsequent potential for recovery would have been correspondingly larger.
Prices in Japan did fall steeply during the Great Recession (2008-10) but the perceived potential for recovery was squeezed by the Obama Monetary Experiment (the Fed’s QE) which meant an immediate slide of the US dollar. It was in response to the related spike of the yen that Prime Minister Abe prepared his counter-stroke. This involved importing the same deflation-phobic inflation-targeting policies that the Obama Federal Reserve was pursuing. Washington could hardly criticize Tokyo for imitating its own monetary experiment.
Deflation and “The Lost Decade”
The architects of the Obama Monetary Experiment have cited as justification Japan’s “lost decade” and the supposed source in deflation. In fact, though, the only period during which the Japanese economy underperformed other advanced economies (as measured by the growth of GDP per capita) was from 1992-97. The underperformance of that period had everything to do with insufficient price and wage flexibility downward, the Clinton currency war, and the vast malinvestment wrought by the prior asset price inflation, coupled with a risk-appetite in Japan shrunken by the recent experience of bust.
Moreover, as time went on, from the early 1990s, huge investment into the Tokyo equity market from abroad compensated for ailing domestic risk appetites. Yes, Japan’s economy could have performed better than the average of its OECD peers if progress had been made in de-regulation, and if Japan had had a better-designed framework of monetary stability to insulate itself from the Greenspan-Bernanke asset price inflation virus of the years 2002-07. (The Greenspan-Bernanke inflation caused speculative temperatures in the yen carry trade to reach crazy heights.) But deflation was never an actual or potential restraint on Japanese prosperity during those years.
True, there was a monetary malaise. Japan’s price stability was based on chance, habit, and economic sclerosis rather than the wisdom of its monetary policy. It had been the huge appreciation of the yen during the Clinton currency war that had snuffed out inflation. Then the surge of cheap imports from China had worked to convince the Japanese public that inflation had indeed come to an end. Lack of economic reform meant that the neutral rates of interest remained at a very low level and so the Bank of Japan’s intermittent zero rate policies did not stimulate monetary growth.
The monetary system in Japan had no secure pivot in the form of high and stable demand for non-interest bearing high-powered money. In Japan the reserve component of the monetary base is virtually indistinguishable from a whole range of close substitutes and banks had no reason to hold large amounts of this (given deposit insurance and the virtual assurance of too-big-to-fail help in need). Monetary policy-making in Japan meant highly discretionary manipulation of short-term interest rates in the pursuance of fine-tuning the business cycle rather than following a set of rules for monetary base expansion.
The Yen After Abenomics
When Prime Minister Abe effected his coup against the old guard at the Bank of Japan there was no monetary constitution to flout. Massive purchases of long-dated Japanese government bonds by the Bank of Japan are lowering the proportion of outstanding government debt held by the public in fixed-rate form. But this is all a slow-developing threat given a gross government debt to GDP ratio of around 230 percent and a current fiscal deficit of 6 percent of GDP. Bank of Japan bond-buying has strengthened irrational forces driving 10-year yields down to almost 0.5 percent despite underlying inflation having risen to 1 percent per annum.
It is doubtless the possibility of an eventual monetization of government debt has been one factor in the slump of the yen. More generally, as the neutral level of interest rates in Japan rises in line with demographic pressures (lower private savings, increased social expenditure) one might fear that BoJ manipulation of rates will eventually set off inflation. Part of the yen’s slump, though, is due to a tendency for that currency to fall when asset price inflation is virulent in the global economy. This stems from the huge carry trade in the yen.
The yen could indeed leap when the global asset price-inflation disease — with its origins in Fed QE — moves to its next phase of steep speculative temperature fall. The yen is now in real effective exchange rate terms at the record low point of the Japan banking crisis in 1997 or the global asset inflation peak of 2007. So, the challenge for investors is to decide when the Abe yen has become so cheap in real terms that its hedge properties make it a worthwhile portfolio component.
Brendan Brown is an associated scholar of the Mises Institute and is author of Euro Crash: How Asset Price Inflation Destroys the Wealth of Nations and The Global Curse of the Federal Reserve: Manifesto for a Second Monetarist Revolution. See Brendan Brown's article archives.
© 2014 Copyright Brendan Brown - All Rights Reserved Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



