Economic Sanctions Not Key Cause of Russia’s Next Recession
Economics / Russia Apr 10, 2014 - 04:14 PM GMTBy: Frank_Shostak
 According to commentators, sanctions imposed by the US and the European Union are pushing Russia toward a recession. However, we hold that some key Russian economic data have been displaying a weakening prior to the annexation of the Crimea to Russia. This raises the likelihood that sanctions might not be the key factor for an emerging recession.
According to commentators, sanctions imposed by the US and the European Union are pushing Russia toward a recession. However, we hold that some key Russian economic data have been displaying a weakening prior to the annexation of the Crimea to Russia. This raises the likelihood that sanctions might not be the key factor for an emerging recession.
The yearly rate of growth of monthly real gross domestic product (GDP) eased to 0.3 percent in February from 0.7 percent in January and 1.8 percent in July last year. After closing at 12.2 percent in March last year the yearly rate of growth of retail sales fell to 7.7 percent in January before settling at 9.6 percent in February.
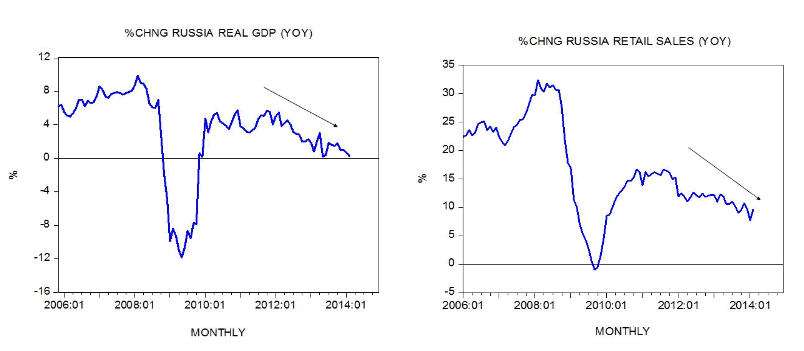
We suggest that the key factor behind any emerging slowdown and a possible recession is a sharp decline in the yearly rate of growth of the money supply (AMS) from 67.1 percent in May 2005 to minus 12.2 percent by September 2009. We hold that the driving force behind this sharp decline is a strong decline in the growth momentum of the central bank’s balance sheet during that period (see chart).
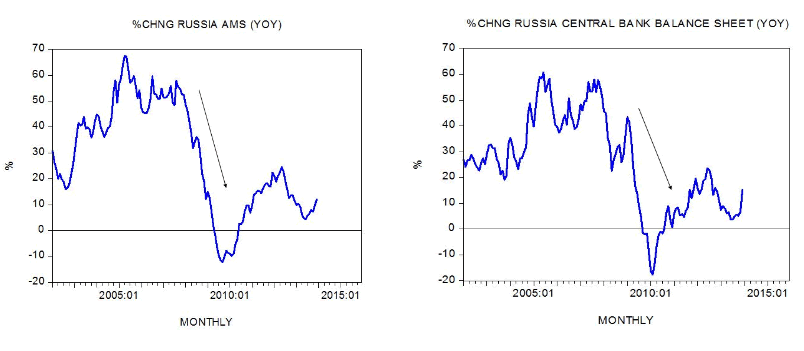
There is a long time lag from changes in the money supply and its effect on economic activity. We suspect that it is quite likely that the effect from a fall in the growth momentum of money during May 2005 to September 2009 is starting to dominate the present economic scene.
This means that various bubble activities that emerged on the back of the prior strong increase in the money supply are at present coming under pressure. So from this perspective irrespective of sanctions, the Russian economy would have experienced a so-called economic slowdown, or even worse, a recession.
Now, to counter a further weakening in the ruble against the US dollar, the Russian central bank has raised the seven day repo rate by 1.5 percent to 7 percent. The price of the US dollar in ruble terms rose to 36.3 in March from 30.8 rubles in March last year — an increase of 18 percent.
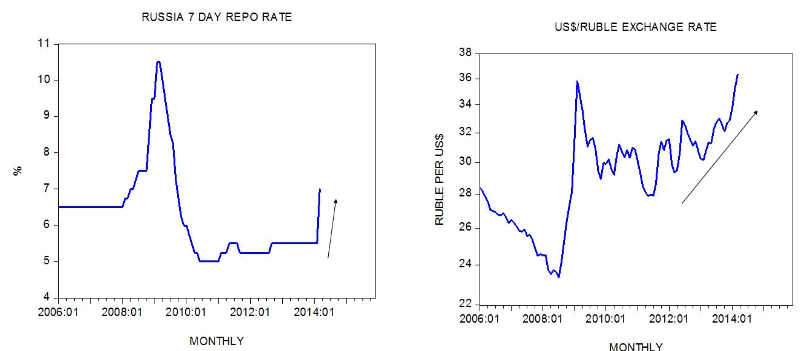
Whilst a tighter interest rate stance can have an effect on the present growth momentum of money supply this is likely to have a minor effect on the emerging economic slowdown, which we suggest is predominately driven by the past money supply.
There is no doubt that if sanctions were to become effective they are going to hurt economic activity in general i.e., both bubble and non-bubble activities.
On this one needs to exercise some caution given the possibility that major world economies are heading toward a slower growth phase.
Hence from this perspective, regardless of sanctions the pace of the demand for the Russian exports is likely to ease.
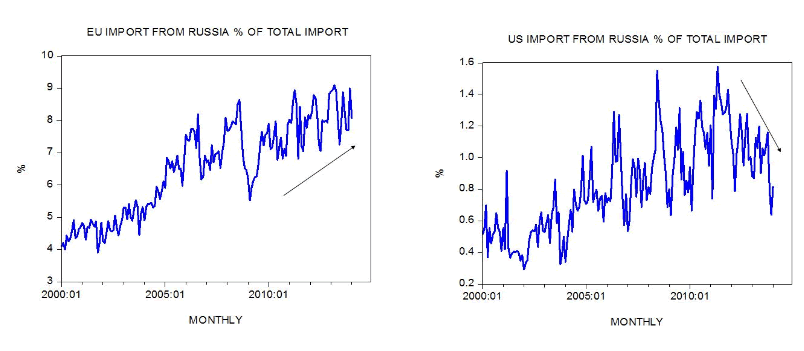
We hold that it is quite likely that the Euro-zone, an important Russian trading partner, is unlikely to enforce sanctions in order to cushion the effect of the possible emerging economic slowdown in the Euro-zone. (Sanctions are likely to have a disruptive economic effect not only on Russia but also on the Euro-zone.) Observe that Russia’s exports to the Euro-zone as a percentage of its total exports stood at 54.1 percent in 2013 against 52.9 percent in 2012. In contrast Russia’s exports to the US as a percentage of total stood at 2.1 percent in 2013. As a percentage of total imports Euro-zone imports from Russia stood at 8 percent in January whilst American imports from Russia as a percentage of total imports stood at 0.8 percent. Note that the Euro-zone relies on Russia for a third of its energy imports. Hence it will not surprise us if the Europeans are likely to be more reluctant than the US in enforcing sanctions.
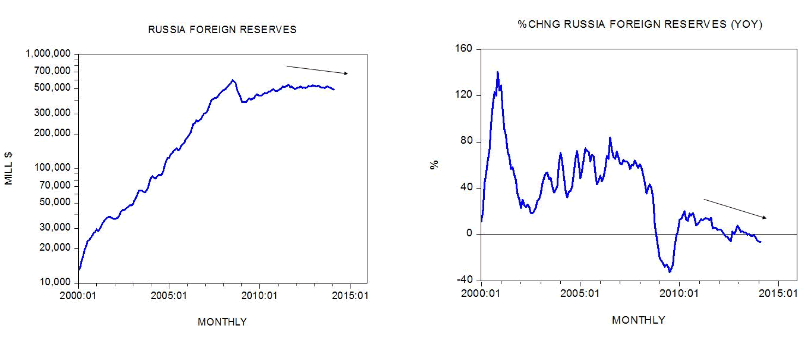
Russia’s foreign reserves have weakened slightly in February from the month before. The level of reserves fell by 1.1 percent to $493 billion after declining by 2.1 percent in January. The growth momentum of reserves also remains under pressure. Year-on-year the rate of growth stood at minus 6.2 percent in February against a similar figure in January. A possible further weakening in China’s economic activity and ensuing pressure on the price of oil is likely to exert more pressure on foreign reserves.
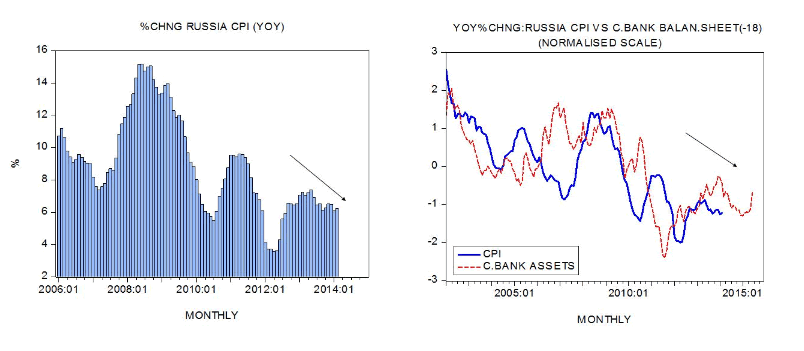
Meanwhile, the growth momentum of the Russian consumer price index (CPI) displays a visible softening. The yearly rate of growth stood at 6.2 percent in February against 6.1 percent in January. Observe that in February last year the yearly rate of growth stood at 7.3 percent. Based on the lagged growth momentum of our Russian monetary measure AMS we can suggest that the yearly rate of growth of the Russian CPI is likely to weaken further in the months ahead.
Summary and Conclusion
According to some experts, sanctions imposed by the US and the European Union are likely to push Russia into a recession. We suggest that the key factor which is likely to push Russia into a recession is not sanctions as such but a sharp decline in the growth momentum of the money supply between May 2005 and September 2009. Given the possibility that major world economies are heading toward a renewed economic slowdown, we suggest that regardless of sanctions the pace of the demand for Russia’s exports is likely to ease. Now, given that the Euro-zone relies on Russia for a third of its energy imports it will not surprise us if the Euro-zone proves likely to be more reluctant than the US in enforcing sanctions.
© 2014 Copyright Frank Shostak - All Rights Reserved Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



