Fed Interest Rate Cuts have Resulted in Surging Commodity Price Inflation
Interest-Rates / Inflation Feb 22, 2008 - 02:30 PM GMTBy: Adrian_Ash
 Six Months of Fun, Fun, Fun from the Fed - "...If Bernanke was expecting a 13% rise on Wall Street, he's got a 45% rise in gold instead – plus a real disaster in US Treasury bond yields..."
Six Months of Fun, Fun, Fun from the Fed - "...If Bernanke was expecting a 13% rise on Wall Street, he's got a 45% rise in gold instead – plus a real disaster in US Treasury bond yields..."
THIS WEEK marked the six-month anniversary of the Fed's first cut to US interest rates during the current world banking crisis.
And it's been fun, fun, fun ever since for hard asset investors.
Aimed at promoting "orderly conditions" in the world of finance, that 0.5% cut to the Fed's discount rate kick-started the sharpest collapse in Dollar interest rates since...well, since last time it tried to restore order to the value of US financial assets.
But while short-term money markets remain tight six months later – and the subprime panic has since spread to "monoline" bond insurers, private equity groups, pan-national banking giants and even US student-loan finance – the only order so far has come in raw materials, rather than finance.
A big fat order of whopper-sized gains, in fact, with a fried egg on top for good measure...
- Crude Oil: +37.5%
- Natural Gas: +29.6%
- Copper: +22.5%
- Platinum: +72.0%
- Silver: +45.1%
- Wheat: +66.5%
- Soybeans: +68.4%
The price of Gold meantime – whose only real utility, unlike all other natural resources, is as a store of value – has now risen in twenty of the last 27 weeks. Spot Gold Prices have gained 44.7% since the morning of August 17th, just before the Fed announced its "extra-ordinary" rate change.
Whereas the S&P500 stock index has dropped 7.5% of its value. Which surely wasn't the plan.
"Even the casual observer can have no doubt that FOMC decisions move asset prices, including equity prices," said Ben Bernanke in a speech of Oct. 2003. "Estimating the size and duration of these effects, however, is not so straightforward."
Then a mere Fed governor, rather than the big cheese himself, Bernanke related a pile of highly detailed and utterly pointless research he'd done with Kenneth Kuttner of the NY Fed. In short: "The statistical evidence is strong for a stock price multiplier of monetary policy of something between 3 and 6, the higher values corresponding to policy changes that investors perceive to be relatively more permanent. That is, according to our findings, a surprise easing by the Fed of 25 basis points will typically lead broad stock indexes to rise from between 3/4 percentage point and one-and-a-half percentage points."
Oh sure, Bernanke was talking about the kind of gains he'd expect to see inside one day ! But slashing the Fed funds target by 225 basis points since the global banking crisis provoked him to act back in August, Bernanke hasn't even got 6.75% across six months...let alone a 13.5% rise on Wall Street.
He's got a surge in the cost of living instead, driven by basic raw material prices. And that's bad news – as in gruesome – for Treasury bond owners.
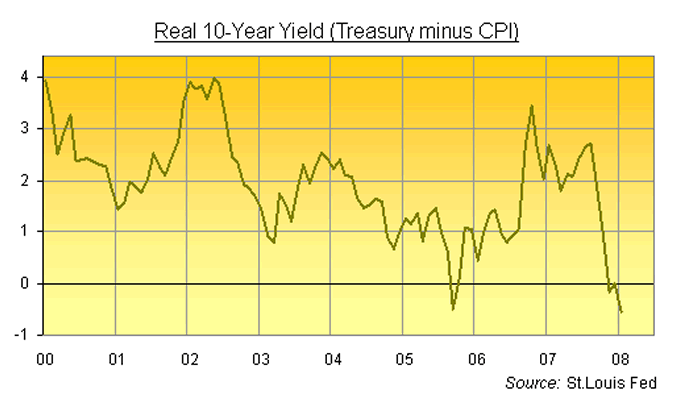
Yes, the Fed's overnight lending rate – as well as short-term Treasury bond yields – tipped sharply negative after accounting for inflation during the Greenspan "emergency" of 2002 to 2005.
But longer-dated US Treasuries – those bonds used to fund the vast bulk of Washington 's on-going finance needs – only briefly failed to keep pace with the cost of living. Unlike now.
Today they're lagging inflation, and threatening to lag it badly.
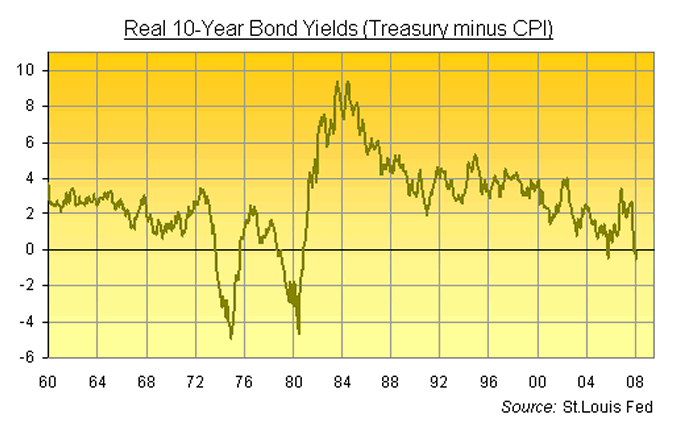
The last time US Treasuries paid a whole lot less than inflation, the crisis got so bad that government bonds became known as "certificates of confiscation".
Money failed to flee into equities, however, even as the United States faced the very real prospect of being unable to find the cash to fund its government spending. To fix this mess in the world's No.1 economy, it took a collapse in nominal bond prices – driven by record-high interest rates from the Fed – and the longest recession since the 1930s depression to restore America 's credit.
Just how miserable might the real returns paid to bond-buyers become if inflation keeps rising today? The runaway producer price index, backed up with $100 crude stood right behind it wearing knuckle-dusters, growls that things are about to get ugly.
And just how far might hard asset prices go as investors flee stocks, bonds, cash and property all at once...?
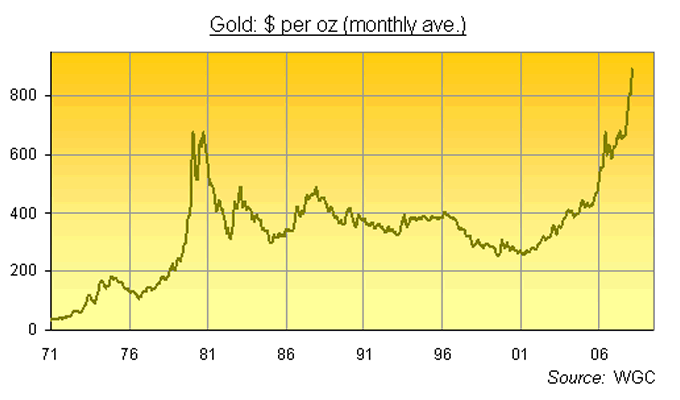
Yes, the current surge in Gold Prices looks a lot like that infamous "cathedral top" of 1980, right?
Gold spiked above $850 per ounce in the spot market on 21st Jan. 1980 ...and then fell almost every year for the next two decades.
But the move above $800 per ounce came and went inside three days. And the run-up saw Gold Prices more than triple on their monthly average in little more than a year. Here in Feb. 2008 – and with US Treasury yields turning negative once again – gold has taken more than half-a-decade to repeat that feat.
Too much, too fast? With Bernanke at the Fed – and $100 oil heading for the pumps, as well as for real bond yields – just maybe we ain't seen nothing yet.
By Adrian Ash
BullionVault.com
Gold price chart, no delay | Free Report: 5 Myths of the Gold Market
City correspondent for The Daily Reckoning in London and a regular contributor to MoneyWeek magazine, Adrian Ash is the editor of Gold News and head of research at www.BullionVault.com , giving you direct access to investment gold, vaulted in Zurich , on $3 spreads and 0.8% dealing fees.
(c) BullionVault 2008
Please Note: This article is to inform your thinking, not lead it. Only you can decide the best place for your money, and any decision you make will put your money at risk. Information or data included here may have already been overtaken by events – and must be verified elsewhere – should you choose to act on it.
Adrian Ash Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



