Godzilla Will Come Out of Tokyo Bay Before Japan Economy and Stock Market Rebounds
Economics / Japan Economy Feb 02, 2012 - 10:55 AM GMTBy: Money_Morning
 Keith Fitz-Gerald writes:
Let's talk Japan.
Keith Fitz-Gerald writes:
Let's talk Japan.
Every year some analyst comes out with a variation of the story that Japan is about to rebound.
Usually the argument goes something like this: Japanese markets are impossibly cheap and the central bank will be there to prevent a catastrophe.
Or sometimes there is another variation of the Cinderella story.
Either way, don't hold your breath. Japan posted its first trade deficit since 1980 last year and the big trade surpluses needed to drive the Nikkei back to its glory days are over.
At best, Japan is going to see balanced trade figures or a small surplus in the years ahead. It won't be enough.
If you're not familiar with what a trade deficit is, here's what you need to know: Japan imported $32 billion worth of stuff more than it exported for the first time in 31 years.
Fighting the Demographic Tide
Critics say there are mitigating factors behind the figures and they're right.
Against the backdrop of one of the world's fastest aging populations, one of the lowest birth rates on the planet, a renewed reliance on foreign energy, and a yen that is so expensive that Japanese corporations are offshoring production, it won't be long before the country eventually plows through its savings.
So $32 billion is just the beginning...
In fact, we are more likely to see Godzilla walk out of Tokyo Bay than we are to witness a return to Japan's halcyon days.
Worse, I believe that within the next five years, Japan will long for the good old days when the trade deficit was merely $32 billion, instead of $100 billion, $200 billion or worse.
Not one of the things I've just mentioned - that the critics cite as short-term influences - are anything but continuations of much longer-term trends. Nearly all of them are being driven by Japan's declining population.
You may not know this, but Japan's population is projected to shrink by 30% by 2060. That means the total population will go from 128 million people today to only 87 million people in less than 50 years.
That's hard to imagine since Japan is one of the most densely populated countries on the planet. But the effects are already visible.
In my neighborhood in Kyoto, for example, we see abandoned houses that fall in on themselves after people die and there are no longer any other family members to live there. We see schools that are shut down in the region because there are no kids to attend them.
We're also seeing companies shuttered because there are no markets for their products, including my wife's family kimono business, which closed after 300 years in existence.
Simply put, you just can't grow a population or its stock markets without people.
Japan also has no immigration policy to speak of, so there is no means of replacing the "silvers," or senior workers, who are leaving their productive years behind them.
By 2060 the number of people who are 65 or older is going to double. At the same time, the number of people in the workforce between 15 and 65 is going to shrink to less than 50% of the total population.
By 2050, there will be 75 retirees for every 100 workers. By comparison, in the United States in 2050 there will be about 32 retirees per 100 workers.
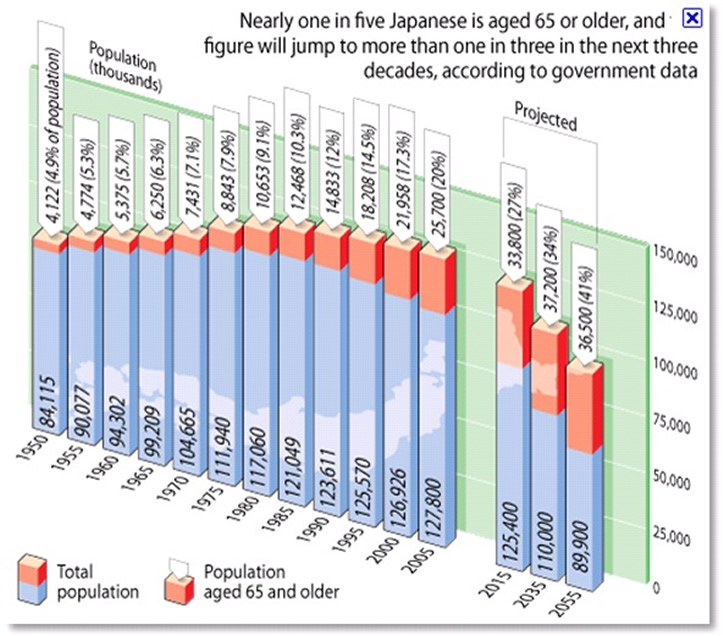
Figure 1: Source: mtholyoke.edu
You'd think Japan could get "busy" and produce more children but even that's problematic. The country has one of the lowest birthrates on the planet. Many young Japanese simply don't want romance -- let alone children.
In fact, many Japanese don't even want sex.
As reported by CNBC, one AFPstudy reported that 36.1% of teenage boys between the ages of 16 and 19 have no interest in sex. That study in 2010 reflected results that were double the 17.5% reported only two years earlier. Girls are even worse, with more than 59% in the same age group reporting no interest.
Things are so bad according to one study I've seen, that at the current birth rate the last Japanese person will be born 953 years from now.
Game Over For Japan?
Critics challenge this assumption, arguing that somehow Japan's hyper-aged will reinvigorate the economy in an orgy of retirement spending and consumption.
That depends on generous pensions and an intact financial system - neither of which Japan has at the moment.
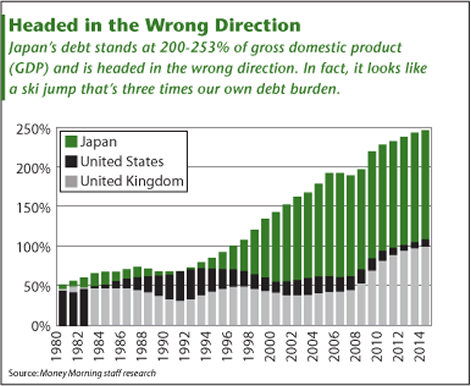
Japan's debt stands at 200% - 253% of GDP, depending on which studies you read, and is headed in the wrong direction. In fact, it looks like a ski jump that's three times our own debt burden.
Senior citizens I know are doing everything they can to hang onto their jobs for as long as they can.
As a result, there is literally nowhere for younger workers to go... except into low value "arubaito" or part-time work with no benefits, no promotions and very little economic value to contribute to Japan's recovery.
My nephew, for example, struggled for years in such a job before getting training and finding work as a mechanic for Mazda.
To be fair, Japanese citizens purchase approximately 95% of Japanese debt. That's why the country has been able to hang on and has not had its own Greek holiday.
By contrast, we borrow about 50% of our money as a nation from overseas, and we're dangerously close to our own version of Greece's meltdown.
But as the number of retirees rises and the number of workers falls, the Japanese government is going to have challenges maintaining this internal funding capacity.
At some point - either because there are not enough debt buyers or rates rise too high - they'll have to turn to external creditors and interest rates that could easily be double the 1.5% the Japanese government pays lenders now.
At that point, debt payments would consume more than half of all government revenue according to The Atlantic.
And then it's game over.

So what's an investor to do? Well for one thing, I sure as hell wouldn't invest in Japan on anything other than an extremely short-term basis.
Despite the fact that trade deficit numbers may ping-pong back into positive territory in the months ahead, there's no reversing the current long-term trend.
The notion that the Nikkei is somehow undervalued is naïve if you do not take the population and its effect on debt into account.
While it is true there may be short bursts of growth, there's no ignoring the fact that the bellwether index is trading at 8,802.51, or 77% below the high it achieved in 1990 and 12% below where it started in 1984.
With very few exceptions, money invested in Japan is going to get trapped there.
That's why, unless you've got money to burn, you can say "sayonara" to Japan.
Source http://moneymorning.com/2012/02/02/godzilla-will-come-out-of-tokyo-bay-before-japan-rebounds/
Money Morning/The Money Map Report
©2012 Monument Street Publishing. All Rights Reserved. Protected by copyright laws of the United States and international treaties. Any reproduction, copying, or redistribution (electronic or otherwise, including on the world wide web), of content from this website, in whole or in part, is strictly prohibited without the express written permission of Monument Street Publishing. 105 West Monument Street, Baltimore MD 21201, Email: customerservice@moneymorning.com
Disclaimer: Nothing published by Money Morning should be considered personalized investment advice. Although our employees may answer your general customer service questions, they are not licensed under securities laws to address your particular investment situation. No communication by our employees to you should be deemed as personalized investent advice. We expressly forbid our writers from having a financial interest in any security recommended to our readers. All of our employees and agents must wait 24 hours after on-line publication, or after the mailing of printed-only publication prior to following an initial recommendation. Any investments recommended by Money Morning should be made only after consulting with your investment advisor and only after reviewing the prospectus or financial statements of the company.
Money Morning Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



