Mainstream Media Blackout on Nuclear Incident at Fort Calhoun Nebraska?
Politics / Nuclear Power Jun 23, 2011 - 04:46 AM GMT Since flooding began on June 6th, there has been a disturbingly low level of media attention given to the crisis at the Fort Calhoun Nuclear Facility near Omaha, Nebraska. But evidence strongly suggests that something very serious may have happened there.
Since flooding began on June 6th, there has been a disturbingly low level of media attention given to the crisis at the Fort Calhoun Nuclear Facility near Omaha, Nebraska. But evidence strongly suggests that something very serious may have happened there.
Unfortunately for members of the public, there is no shortage of proof that serious nuclear incidents and radiation releases have happened in America, and have been covered up each and every time. For this reason, it is paramount that the media and the public demand every bit of information available on this latest event.
First accounts tell us that on June 7th, there was a fire reported at Fort Calhoun. The official story is that the fire was in an electrical switchgear room at the plant. The apparently facility lost power to a pump that cools the spent fuel rod pool, allegedly for a duration of approximately 90 minutes.
FORT CALHOUN NUKE SITE: does it pose a public risk?
The following sequence of events is documented on the Omaha Public Power District’s own website, stating among other things, that here was no such imminent danger with the Fort Calhoun Station spent-fuel pool, and that due to a fire in an electrical switchgear room at FCS on the morning of June 7, the plant temporarily lost power to a pump that cools the spent-fuel pool.
In addition to the flooding that has occurred on the banks of the Missouri River at Fort Calhoun, the Cooper Nuclear Facility in Brownville, Nebraska may also be threatened by the rising flood waters.
As was declared at Fort Calhoun on June 7th, another “Notification of Unusual Event” was declared at Cooper Nuclear Station on June 20th. This notification was issued because the Missouri River’s water level reached an alarming 42.5 feet. Apparently, Cooper Station is advising that it is unable to discharge sludge into the Missouri River due to flooding, and therefore “overtopped” its sludge pond.
Not surprisingly, and completely ignored by the Mainstream Media, these two nuclear power facilities in Nebraska were designated temporary restricted NO FLY ZONES by the FAA in early June. The FAA restrictions were reportedly down to “hazards” and were ‘effectively immediately’, and ‘until further notice’. Yet, according to the NRC, there’s no cause for the public to panic.
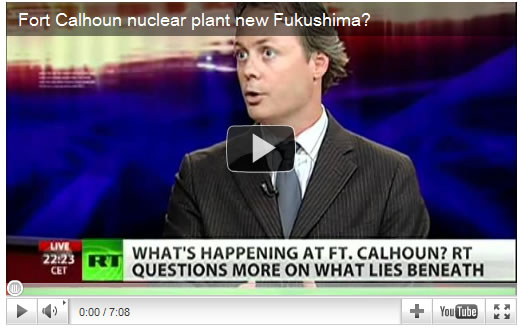
FORT CALHOUN: Under water now. Is it potentially the next Fukushima?
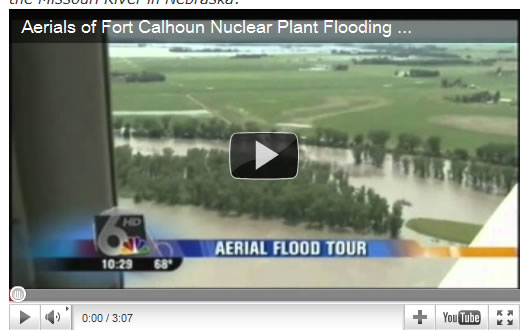
A news report from local NBC 6 on the Ft. Calhoun Power Plant and large areas of farm land flooded by the Missouri River, interviews a local farmer worried about the levees, “We need the Corps-Army Corps of Engineers–to do more. The Corps needs to tell us what to do and where to go. This is not mother nature, this is man-made.” Nearby town Council Bluffs has already implemented its own three tier warning system should residents be prepared to leave the area quickly.
“On June 6, 2011, the Federal Aviation Administration(FAA) put into effect ‘temporary flying restrictions’or a NO FLY ZONE – until further notice over the area around Fort Calhoun Nuclear Power Plant in Blaine, Nebraska.”
To date, it is unknown to members of the public whether or not the incident at Ft Calhoun Nuclear is actually a Level 4 emergency (on a US regulatory scale). A Level 4 emergency would constitute an “actual or imminent substantial core damage or melting of reactor fuel with the potential for loss of containment integrity.”
If there was any core damage, there is no guarantee that officials would allow such information to be made public for fear of public panic and loss of confidence. Serious nuclear incidents have taken place on US soil which were covered-up, in some cases for over 40 years. “In 1959, a partial meltdown occurred at the Boeing-Rocketdyne nuclear testing facility, about 30 miles northwest of downtown Los Angeles. The incident released the third greatest amount of radioactive iodine in nuclear history. But no one really heard about it until Boeing recently settled a class-action suit filed by local residents,” reported Living On Earth in 2006. At no point were members of the public informed about these severe radiation leaks which undoubtedly caused hundreds of cases of cancer and contributed to resident deaths. Details of this and other incidents have been kept secret for some 40 or more years.
COVER-UP: The Boeing-Rocketdyne nuclear incident, 30 miles from downtown Los Angeles.
According to the seven-level International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale, a Level 4 incident requires at least one death, which has not occurred according to available reports.
According a recent report on the People’sVoice website, The Ft. Calhoun plant — which stores its fuel rods at ground level according to Tom Burnett – is now partly submerged and Missouri River levels are expected to rise further before the summer if finished, local reports in and around the Fort Calhoun Nuclear Plant suggest that the waters are expected to rise at least 5 more feet.
Burnett states, “Ft. Calhoun is the designated spent fuel storage facility for the entire state of Nebraska…and maybe for more than one state. Calhoun stores its spent fuel in ground-level pools which are underwater anyway – but they are open at the top. When the Missouri river pours in there, it’s going to make Fukushima look like an X-Ray.”
The People’s Voice’s report explains how Ft Calhoun and Fukushima share some of the very same high-risk factors:
“In 2010, Nebraska stored 840 metric tons of the highly radioactive spent fuel rods, reports the Nuclear Energy Institute. That’s one-tenth of what Illinois stores (8,440 MT), and less than Louisiana (1,210) and Minnesota (1,160). But it’s more than other flood-threatened states like Missouri (650) and Iowa (420).”
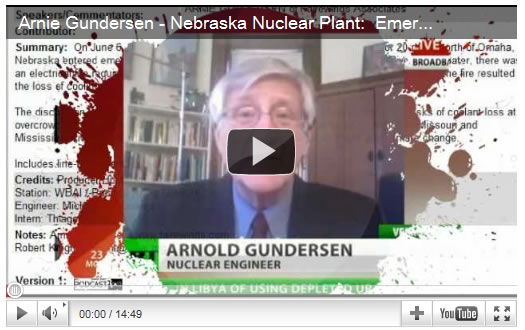
Nuclear engineer Arnie Gundersen explains how cooling pumps must operate continuously, even years after a plant is shut down.
Conventional wisdom about what makes for a safe location regarding nuclear power facilities was turned on its head this year following Japan’s Fukushima disaster following the earthquake and tsunami which ravaged the region and triggered one of the planets worst-ever nuclear meltdowns.
As was the critical event in Fukushima, in Ft Calhoun circulating water is required at all times to keep the new fuel and more importantly the spent radioactive material cool. The Nebraska facility houses around 600,000 – 800,000 pounds of spent fuel that must be constantly cooled to prevent it from starting to boil, so the reported 90 minute gap in service should raise alarm bells.
TV and radio journalist Tom Hartmann explores some of these arguments here:
Nebraska’s nuclear plant’s similarities to Japan’s Fukushima, both were store houses for years of spent nuclear fuel rods.
The nuclear industry has a very long history of withholding information and misleading the public with regards to the hazards of its industrial activities. One of the lessons we can learn for Japan’s tragic Fukushima disaster is that the government’s choice to impose a media blackout on information around the disaster may have already cost thousands of lives. Only time will tell the scope the disaster and how many victims it will claim.
Editor Patrick Henningsen
© 2011 Copyright Patrick Henningsen - All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.