IMF Warns U.S. Real Estate Sectors Could Bring Banking Crisis 2.0
Housing-Market / US Housing Aug 05, 2010 - 02:44 AM GMTBy: Dian_L_Chu
 The International Monetary Fund (IMF) stress tested 53 large banking holding companies and published its findings last month. The report concluded that despite restoration of some stability, there remain certain important risks to the U.S. financial system and economy mainly coming from the real estate sectors:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) stress tested 53 large banking holding companies and published its findings last month. The report concluded that despite restoration of some stability, there remain certain important risks to the U.S. financial system and economy mainly coming from the real estate sectors:
- Further increases in nonperforming loans due to high unemployment rate and significant weakness in the real estate sectors
- Credit quality in the commercial real estate (CRE) sector - About $1.4 trillion of CRE loans will mature in 2010–14, nearly half of which are 90 days or more past due or “underwater.”
- Housing prices - The very high level of underwater mortgages increases the risk of strategic defaults and further losses to banks and mortgage backed security (MBS) investors.
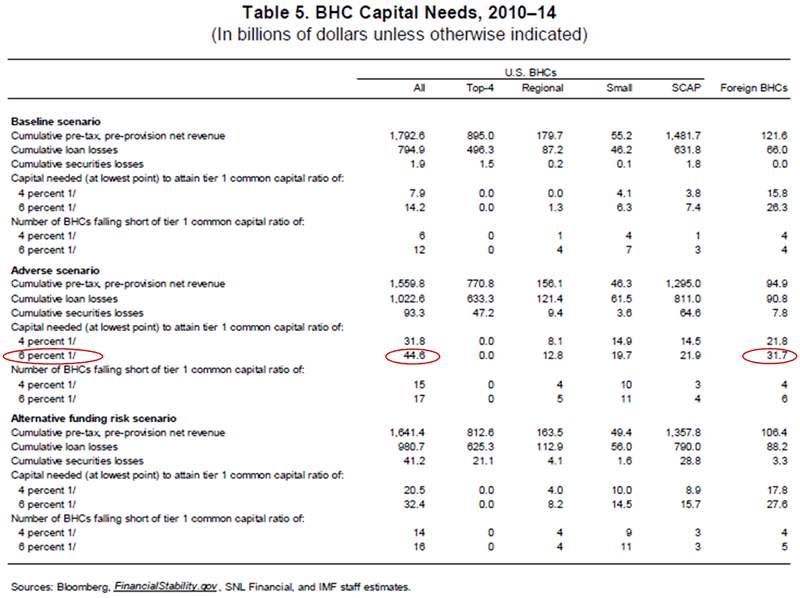
Since bank balance sheets remain fragile and under-capitalized (Figure 1), under an “adverse scenario”, small and regional banks as well as subsidiaries of foreign banks would incur $1.113 trillion of cumulative loan losses from 2010 to 2015 and need as much as $76.3 billion (i.e. a TARP 2.0), additional capital to meet a tier one ratio of 6% .
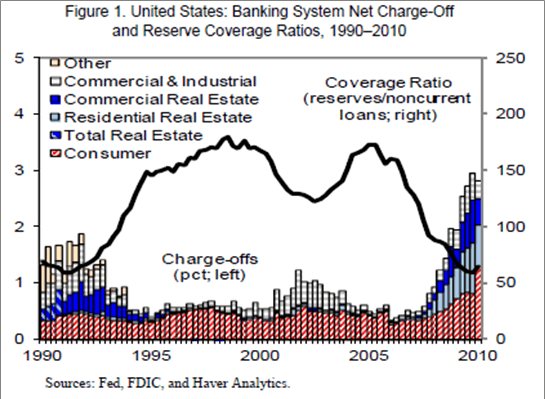
Under the “baseline scenario”, cumulative loan losses would have been $860.9 billion, and need $40.5 billion additional capital. (See table)
“Almost all of the recent issuance of U.S. private label MBSs has comprised re-securitizations of formerly “AAA” senior securities (so-called “re-remics”), with the Fed’s TALF responsible for much of the 2009 issuance of other asset backed securities (ABSs).”
And to make things even more depressing, IMF warned that
Other research reports also paint an equally gloomy picture. According to an analysis by Realpoint, reported by HousingWire, delinquencies in commercial mortgage -backed securities (CMBS) in the US increased to 7.2%, and more than triple the rate a year ago. In May, the total delinquent unpaid balance for these loans reached $57.3 billion.“The economy and some key financial markets continue to depend heavily on fiscal, monetary, and financial policy support, and the output gap is expected to remain wide for many years.”
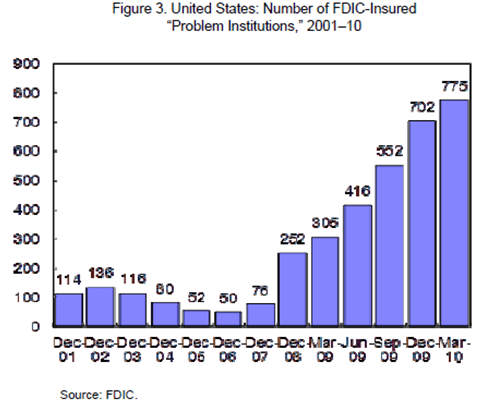
Realpoint forecasts by the end of 2010, the total amount of unpaid principal balance could grow between $80 billion and $90 billion, and the delinquency rate could reach as high as 12%. Earlier in the year, Trepp reported that these spiking delinquencies could cause bank failures to increase as much as 30% in 2010 (You think we don’t have enough problem banks bankrupting FDIC already? see Figure 3)
While the $40-80 billion capitalization numbers probably will not take the entire U.S. economy into a double-dip recession, they will likely put a significant drag on GDP and earnings in the financial sector, as well as the broader equity market for the next two to six quarters.
With the easy year-over-year earnings beat coming to an end, the best of the earnings may have already come to pass. As such, now would be a good time to take some profit off the table for another day, another entry point.
Dian L. Chu, M.B.A., C.P.M. and Chartered Economist, is a market analyst and financial writer regularly contributing to Seeking Alpha, Zero Hedge, and other major investment websites. Ms. Chu has been syndicated to Reuters, USA Today, NPR, and BusinessWeek. She blogs at Economic Forecasts & Opinions.
© 2010 Copyright Dian L. Chu - All Rights Reserved Disclaimer: The above is a matter of opinion provided for general information purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Information and analysis above are derived from sources and utilising methods believed to be reliable, but we cannot accept responsibility for any losses you may incur as a result of this analysis. Individuals should consult with their personal financial advisors.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



