Why Deflation … Not Inflation … Remains the Problem
Economics / Deflation Aug 01, 2009 - 03:06 AM GMT Bryan Rich writes: Currency values are highly influenced by interest rates … a key driver in determining the flow of global capital.
Bryan Rich writes: Currency values are highly influenced by interest rates … a key driver in determining the flow of global capital.
For example, if you lived in Japan for the past decade, you would have experienced a decade of near-zero interest rates. Therefore, you might have shopped outside your home country for a better return on your money.
And that’s exactly what droves of hedge funds did — selling the yen to buy higher yielding currencies that paid them 5, 6, 7 percent and even much more on their money. This became known as the very popular and very crowded “carry trade.”
 |
| When times are good, central banks might boost interest rates to prevent runaway inflation. |
In good economic times, countries that are trying to cool down a robust and growing economy often maintain higher interest rates relative to countries that are trying to stimulate growth. It’s within these hearty economies that global capital tends to gravitate for the benefit of the higher yield. And this demand for higher yield tends to have a positive effect on the currency.
Other countries could be forced to pay higher interest rates because of the risk associated with their economies. For instance, they might have tenuous inflationary or political problems that make it difficult to attract investment capital.
But regardless of the higher risks, investors could still find such opportunities attractive … for the right price (i.e. yield).
The current environment for global investors, however, is much different …
- The carry trade has been decimated …
- Global growth has collapsed …
- And global central banks have responded to the crisis and the worst global recession in 60 years by cutting interest rates to the bone.
In this crisis era, the primary focus for currency market participants hasn’t been yield … it’s been safety. But now that risk appetite has returned, sentiment is shifting toward relative economic stability, prospects for growth, value and again, yield.
ZIRP, Deflation and Elevated Risk
Japan was the pioneer of a zero interest rate policy (ZIRP) after experiencing decade-long bouts with recession. Now, the rest of the developed world has followed.
Since late 2007, the U.S. has cut its benchmark overnight lending rate by 5 percentage points to 0.25 percent. The UK chopped its rate by 5.25 percentage points to 0.50 percent. Switzerland, Canada, Japan all sit at or near zero interest rates. And the Eurozone followed, slowly but surely, whittling rates down from 4.25 percent to 1 percent — and moving its key deposit rates down to near zero.
Even after aggressive rate cuts and other efforts by central banks to pump money into their economies and despite all of the chatter about the Fed’s plans to deal with future inflation … deflation remains the problem, not inflation.
Prices are falling in half of the twenty largest economies in the world!
For instance, as you can see in the chart below, year-over-year prices in the U.S. have fallen the most in 60 years.
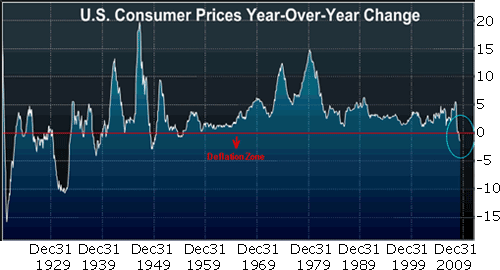
Source: Bloomberg
In Germany, deflation has hit for the first time in 22 years. And it doesn’t stop there: Consumer prices in Japan, China, France, Spain, Canada, Switzerland, Ireland, Hong Kong and Singapore are falling.
And just this week: Italy joined the ranks, reporting its first drop in prices since 1959 … Japan reported a continued fall in prices … and the Eurozone recorded its biggest price drop on record.
Many think that the central banks, particularly the Fed, have done too much tinkering with the money supply spigot, consequently setting a date with runaway inflation.
 |
| The Fed’s job is not easy: Stimulate growth while keeping inflation in check. |
But my question is this: Have central banks done enough with interest rates to stop prices from moving lower and to get economic growth back on track?
Contrary to all of the attention that has been placed on plans for removing monetary stimulus, the popular Taylor rule in economics suggests that interest rates in the U.S. should be much lower … well into negative territory. In fact, Goldman Sachs sees the appropriate level for short-term rates at minus 5.8 percent.
Since official interest rates are already near zero, does that mean the global printing presses will have to continue running? Does this rule imply that we can expect more severe deflation ahead?
During the Great Depression, prices fell for four straight years. For two of those years, prices were down 10 percent. But in the world of fiat currencies, central banks have the ammunition of the printing press to fend off such a nasty downward spiral.
However, with increasing global debt burdens, central banks are also scrutinized under a microscope and face massive political forces that may limit the firing of their ammunition.
This changing dynamic from inflation to deflation in a zero-interest-rate world creates interesting global yield comparisons when adjusted for prices. Of course nominal interest rates in major economies are virtually zero. But when normalized, to adjust for deflation (or inflation for some countries), the real yields paint a very different picture. In fact, in stark contrast to what most might expect, the U.S. and Japan join China and Brazil in having the highest real interest rates among the world’s largest countries.
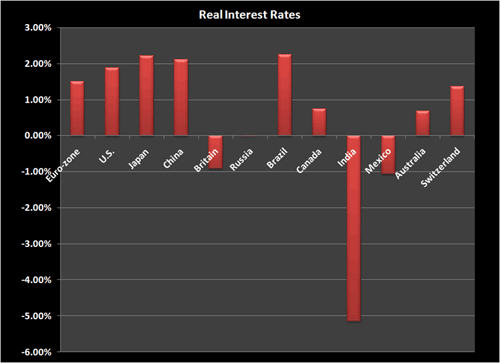
Source: Bloomberg
And with global investors starved for yield, these countries with relative yield advantages, especially those bolstered with the additional advantage of liquidity and relative safety should attract capital. Most importantly, their currencies should benefit!
Asset prices across the globe have staged an aggressive recovery over the past five months. Nevertheless, continued downward pressure in global prices could prove this upswing in financial markets to be a simple retracement in a longer-term trend back to pre-bubble levels. So keep a close eye on the deflation dynamic … and real yields.
Regards,
Bryan
P.S. I’m now on Twitter. Please follow me at http://www.twitter.com/realbryanrich for frequent updates, personal insights and observations from my travels around the world.
If you don’t have a Twitter account, sign up today at http://www.twitter.com/signup and then click on the ‘Follow’ button from http://www.twitter.com/realbryanrich to receive updates on either your cell phone or Twitter page
This investment news is brought to you by Money and Markets . Money and Markets is a free daily investment newsletter from Martin D. Weiss and Weiss Research analysts offering the latest investing news and financial insights for the stock market, including tips and advice on investing in gold, energy and oil. Dr. Weiss is a leader in the fields of investing, interest rates, financial safety and economic forecasting. To view archives or subscribe, visit http://www.moneyandmarkets.com .
Money and Markets Archive |
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.



