Pakistan Floods, From Natural Disaster to Social Catastrophe
Politics / Pakistan Aug 17, 2010 - 08:12 AM GMTBy: Global_Research
 Snehal Shingavi writes: The floods which have devastated huge areas of Pakistan may be an act of nature, but the worsening humanitarian crisis that followed is a direct result of the failures of Pakistan's venal leaders – and the impact of the U.S. “war on terror.”
Snehal Shingavi writes: The floods which have devastated huge areas of Pakistan may be an act of nature, but the worsening humanitarian crisis that followed is a direct result of the failures of Pakistan's venal leaders – and the impact of the U.S. “war on terror.”
According to official estimates, more than 20 million people have been displaced and another 1,600 are dead as a result of one of the worst floods in Pakistani history. In some places, the rains have made the Indus River 15 miles wide, some 25 times broader than normal.
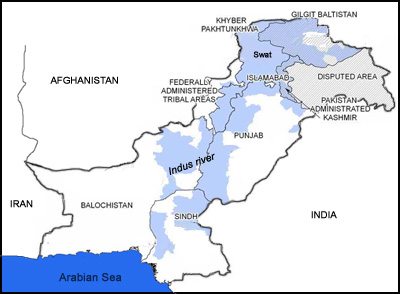
The flooding started when the monsoon rains tore through the mountains in the northwest part of the country (called Khyber-Pukhtunkhwa). As the waters raged through the Sindh and Punjab provinces, they destroyed hundreds of thousands of homes and over 1.7 million acres of farmland. Several large cities were also been submerged, like Naushera, Muzaffarabad and Abottabad. The people who have made it out of the flood-ravaged areas are crammed in makeshift shelters or in overcrowded government buildings.
Those who escaped the floods find themselves without access to food, clean drinking water, sanitation and medicine. All of this has exacerbated the crisis, as many more are likely to die as the result of diarrhea, cholera and other diseases.
Affected Areas
 Getting aid to many of the areas affected by the flooding has also been difficult, as the floods wiped out much of the infrastructure that relief agencies need: power stations have been flooded, gas lines have been ripped out, and grain storage areas have been made irrelevant.
Getting aid to many of the areas affected by the flooding has also been difficult, as the floods wiped out much of the infrastructure that relief agencies need: power stations have been flooded, gas lines have been ripped out, and grain storage areas have been made irrelevant.
Particularly disheartening is the fact that many of the people who now find themselves homeless are the very same who were forced out of their homes last year during the Pakistani military campaign in Swat against the Taliban and its allies in the region. Every single bridge in Swat has been wiped out, and many of the houses that were rebuilt after American drones bombed the area have again been destroyed. Moreover, Pakistan still hasn't fully recovered from the effects of a particularly deadly earthquake in 2005.
Two interconnected factors have made the flooding itself worse. First, the number of incidents of extreme weather in Pakistan has increased in the past several years, a fact that many scientists attribute to the effects of global climate change. Many commentators have linked the devastation in Pakistan to the landslides in China and flooding in Bangladesh, as part of a vast change in regular weather patterns in the region.
Second, the massive dam and canal network that threads through Pakistan was built in the interests of large landowners and big capitalists rather than the people. This has meant that infrastructure repair and emergency relief have been extremely lopsided, and organized around preserving the interests of the landed elite rather than around flood prevention.
Monsoon rains, after all, happen every year, and there have been more than a dozen major floods in Pakistan since the 1970s. Still, flood control remains inadequate.
Network of Canals
 A man evacuates his children through waist-deep waters after heavy flooding in Nowshera, located in Pakistan's northwest Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa Province. A man evacuates his children through waist-deep waters after heavy flooding in Nowshera, located in Pakistan's northwest Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa Province. |
Since the British occupation of India in the 19th century, the rulers of Punjab and Sindh tried to transform an arid landscape into a rich agricultural area by building a network of canals and elaborate irrigation arteries throughout the region. In Punjab and Sindh, it wasn't the rain that caused the flooding, but rather the fact that there are no large flood control mechanisms built into the irrigation network.
The system has barrages (large dams), but is also dotted with low dams, whose primary function is to divert normal water flows into canals. Yet instead of preparing for the contingency of a flood, the government of Pakistan has been putting up dykes to prop up this bad infrastructure. As a result, floodwaters have been pushed into regions that are ill-equipped to deal with such problems.
As Mushtaq Gaadi, professor at Qaid-e-Azam University in Islamabad put it:
“When the World Bank started its rehabilitation project of Taunsa Barrage three years ago, it was meant basically to rehabilitate and repair the whole barrage. And $140-million were allocated. We asked them to pay attention to ecological issues, and especially the issue of this tilt, the position, sedimentation of the barrage, and how the whole ecology of the barrage is going to change, because its channel has been raised up, and now all the low-lying areas are more in the danger of floods.
“All that has been ignored. Just six months after the rehabilitation project, the barrage failed to hold up the water, and it was breached. So it was, in fact, the failure of Taunsa Barrage that caused such large destruction...
“These are not only natural floods, but the structures that were created were injurious and badly looked after by the irrigation department – they caused such destruction and worsened the situation.”
To make matters worse, naked self-interest has dominated the allocation of resources and the decisions about where and how to act. In one instance in Kot Mittin in southern Punjab, the government built a wall to save a prosperous neighbourhood. But in its attempts to save the Tonsa barrage, it managed to submerge the poor neighbourhood next to it. Some 100,000 people lost their homes in the process.
Even more damning has been the activity of landlords in Sindh who have been cutting slits into the banks of the canals in order to save their own lands. In the process of securing the Guddu Barrage in Sindh, the landlords managed to drown the people of Jacobabad. And there are reports of politicians, like Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gilani, diverting relief aid from the most needy sections of Pakistan to their own home districts.
State Corruption
This will have a series of social and political consequences in Pakistan. First, it has raised serious challenges about the ability of the Pakistani state to provide for its own people. Aside from the fact the nation depends on a huge injection of international aid to remain economically afloat, much of the international aid that the country does receive goes into the coffers of the military.
To add insult to injury, Pakistani politicians, including President Asif Ali Zardari, were nowhere to be found for several days while millions of Pakistanis suffered. As a sign of the growing rage that people feel, Hina Rabbani Kher, a junior minister from the Pakistan People's Party, was pelted with stones by protesters after being absent for a week after the flooding began from her constituency in Punjab.
As Fatima Bhutto, the niece of the former Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto, argued:
“The entire upper echelon of the Pakistani state has traveled to Europe and to Dubai at the expense of the Pakistani people. Zardari has been staying at five-star hotels everywhere he goes. He has been ferried around in private limousines. The security for him and his entourage is privately hired.
“There's no justification for spending that money that Pakistan so desperately needs. And of course, it's ridiculous then to say that the president had to go abroad to lobby for funds for the flood victims, when in fact the flood victims could have benefited from the money that the Pakistani treasury has just spent on this enormously pointless visit.”
Zardari is already seen as widely corrupt by most Pakistanis. His most recent gaffe is likely to work to the benefit of the Pakistani Army, which has been responsible for much of the aid that has been delivered to flood victims.
Second, much of the relief aid will come out of money that has been earmarked for development projects. That means that even if people can survive the next few months (which are likely to be marked by famine and outbreaks), they won't really have lives to return to. Rehabilitation and reconstruction will be forthcoming only in the distant future. There are already signs that this will boil over into mass anger against the Pakistani state. Some commentators are speculating that food riots and major protests are highly likely.
Third, the disaster will only exacerbate the already tense ethnic situation in Pakistan. Over the past few years, a major rift has opened up between the displaced people of Khyber-Pukhtunkhwa (formerly the Northwest Frontier Province) and the people of Sindh and Punjab who see the refugees as drains on their resources and responsible for the rise in Islamic militancy.
The worst part about the humanitarian disaster in Pakistan is the fact that international aid has been very slow in coming. To date, the international community has only managed to offer a measly $150-million in aid. Pakistani officials estimate that they will need billions of dollars in order to manage the crisis.
Some in the American media have suggested that the problem is “donor fatigue” or “Pakistan fatigue” (implying that somehow Pakistani deaths are seen as less important than those caused by other natural disasters). The international community offered $1-billion in aid for earthquake relief in Haiti, for instance, and over $13-billion in aid for tsunami relief in India.
American Imperialism
But the real problem is much simpler: the American ruling establishment has spent the last several years blaming Pakistan for its woes in Afghanistan. This has found an ugly corollary in the already rampant Islamophobia in the U.S. and Europe.
Washington, for instance, manages to give Pakistan $1-billion every year for its help in fighting the Taliban along the Afghan border. But when it comes to humanitarian relief, the U.S. could only find a meager $70-million.
Part of the reason for this paltry sum is that the U.S. is more concerned with its own geopolitical agenda in the region than humanitarian aid. But it also reflects political pressure from the conservative wing of the U.S. political establishment, which blames Pakistan for the American failures in Afghanistan.
Other countries are also providing limited aid. Neighbouring India, for instance, a country well placed to offer substantial assistance to Pakistan, has put political rivalry ahead of humanitarian assistance, offering just $5-million in aid. Political opportunists in India are warning that any aid to Pakistan will go into the hands of “terrorist organizations.”
The ordinary people of Pakistan are caught between the war in Afghanistan that is killing increasing numbers of Pakistanis and the corrupt politicians who are wrecking the economy. The U.S. and Pakistani response to current flooding is a damning indictment of the failure of both governments to provide genuine help to the people of Pakistan. •
Snehal Shingavi is assistant professor at University of California, Berkeley. He writes for SocialistWorker.org, where this article first appeared.
Global Research Articles by Snehal Shingavi© Copyright Snehal Shingavi , Global Research, 2010
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are the sole responsibility of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of the Centre for Research on Globalization. The contents of this article are of sole responsibility of the author(s). The Centre for Research on Globalization will not be responsible or liable for any inaccurate or incorrect statements contained in this article.
© 2005-2022 http://www.MarketOracle.co.uk - The Market Oracle is a FREE Daily Financial Markets Analysis & Forecasting online publication.




